Magnesium And Chlorine Ionic Compound
Ionic and Metallic Bonding
Ionic Bonding
- Ascertain ionic compound.
- Define ionic bond.
- Employ electron dot diagrams to illustrate electron transfer and ionic bond formation.

Does the bounding main really have salt in it?
We can go common table table salt from several sources. It can exist mined in the solid class in salt mines or found every bit a solid in deposits. We can as well become salt from the ocean, but it actually does not exist as salt when in solution. The sodium ions and chloride ions are dissolved, but not combined into a construction until all the water is removed.
Most of the rocks and minerals that make upward the Earth's crust are composed of positive and negative ions held together by ionic bonding. An ionic compound is an electrically neutral compound consisting of positive and negative ions. Y'all are very familiar with some ionic compounds such as sodium chloride (NaCl). A sodium chloride crystal consists of equal numbers of positive sodium ions (Na + ) and negative chloride ions (Cl − ).
Ionic Bonds
Oppositely charged particles attract each other. This bonny strength is often referred to as an electrostatic force . An ionic bond is the electrostatic forcefulness that holds ions together in an ionic compound . The forcefulness of the ionic bond is directly dependent upon the quantity of the charges and inversely dependent on the distance between the charged particles. A cation with a 2+ charge will make a stronger ionic bail than a cation with a 1+ accuse. A larger ion makes a weaker ionic bond considering of the greater distance between its electrons and the nucleus of the oppositely charged ion.
Electron Dot Diagrams
Nosotros will use sodium chloride as an example to demonstrate the nature of the ionic bond and how it forms. As you lot know, sodium is a metal and loses its 1 valence electron to get a cation. Chlorine is a nonmetal and gains one electron in becoming an anion. Both attain a noble-gas electron configuration. Withal, electrons cannot exist simply "lost" to nowhere in particular. A more accurate way to draw what is happening is that a single electron is transferred from the sodium atom to the chlorine atom as shown beneath.
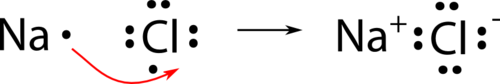
The ionic bond is the attraction of the Na + ion for the Cl − ion. It is conventional to testify the cation without dots around the symbol to emphasize that the original energy level that contained the valence electron is at present empty. The anion is now shown with a complete octet of electrons.
For a compound such as magnesium chloride, information technology is not quite as unproblematic. Considering magnesium has two valence electrons, information technology needs to lose both to achieve the noble-gas configuration. Therefore, two chlorine atoms will be needed.

The last formula for magnesium chloride is MgCl 2 .
Summary
- An ionic chemical compound contains positive and negative ions.
- An ionic bond is electrostatic in nature.
- Electron dot diagrams can be used to illustrate electron movements and ion germination.
Do
Questions
Utilize the link beneath to answer the post-obit questions:
http://chemed.chem.wisc.edu/chempaths/GenChem-Textbook/Ionic-Bonding-565.html
- What do cations and anions class?
- What influences allure for electrons?
- What metals by and large grade ionic bonds?
Review
Questions
- What is an ionic compound?
- What is an ionic bond?
- Which cation (Na + or Ca 2+ ) would form a stronger ionic bond with Cl -
- electrostatic force: Attraction of oppositely charged particles toward i some other.
- ionic bond: The electrostatic forcefulness that holds ions together in an ionic chemical compound.
- ionic compound: An electrically neutral compound consisting of positive and negative ions.
Show References
Magnesium And Chlorine Ionic Compound,
Source: https://www.coursehero.com/study-guides/cheminter/ionic-bonding/
Posted by: jacksonhipild.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Magnesium And Chlorine Ionic Compound"
Post a Comment